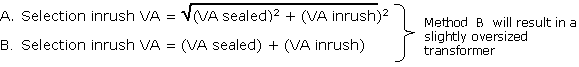Electromagnetic
control components demand inrush currents up to 10 times the transformer's
nominal rating. While this inrush is occurring, the output side of the
transformer must not fall below 85% of nominal as specified by NEMA St.
1, Part 4. Using a transformer that does not meet these ratings may cause
erroneous shutdowns or glitches in products downstream.
For
proper transformer selection, three characteristics of the load circuit
must be determined in addition to the minimum voltage required to operate
the circuit. These are total steady state (sealed) VA, total inrush VA,
and inrush load power factor.
A.
Total steady state (sealed) VA is the volt-amperes that the
transformer must deliver to the load circuit for an extended period
of time.
B.
Total inrush VA is the volt-amperes that the transformer
must deliver upon initial energization of the control circuit. Energization
of electromagnetic devices takes 30-50 milliseconds. During this inrush
period the electromagnetic control devices draw many times normal current
- 3-10 times normal is typical.
C.
Inrush load power factor is difficult to determine without
detailed vector analysis of all the load components. Generally such
an analysis is not feasible. Therefore, a safe assumption is 40% power
factor. Until recently 20% PF was commonly used for transformer selection,
however, tests conducted on major brands of control devices indicate
that 40% PF is more accurate.
Selection
-
Determine the supply and load voltages as well as your required frequency
(i.e. 60Hz). The supply voltage is the available voltage to the control
transformer. The load voltage is the operating voltage of the devices
that will be connected to the transformer output.
-
Calculate the total sealed VA by adding the VA requirements of all
components that will be energized together (timers, contactors, relays,
solenoids, pilot lamps, etc.). Sealed VA data is available from the
control device manufacturer.
-
Add the inrush VA of all components that will be energized together.
Be sure to include the sealed VA of components that don't have an
inrush, (lamps, timers, etc.) as they present a load to the transformer
during maximum inrush.
-
Calculate selection inrush VA in one of the following two ways:
|